Maintaining gum health is a cornerstone of overall oral wellness, yet it is often overlooked amid the focus on sparkling teeth. Healthy gums not only support teeth but also play a vital role in preventing chronic conditions that can extend beyond the mouth. Recent studies suggest that the state of your gums could influence heart health, diabetes management, and even cognitive function, making gum care a topic worthy of attention. In this article, we explore comprehensive strategies, scientific insights, and practical approaches to gum health, offering a detailed roadmap for keeping your gums resilient and functional.
What Will You Read?
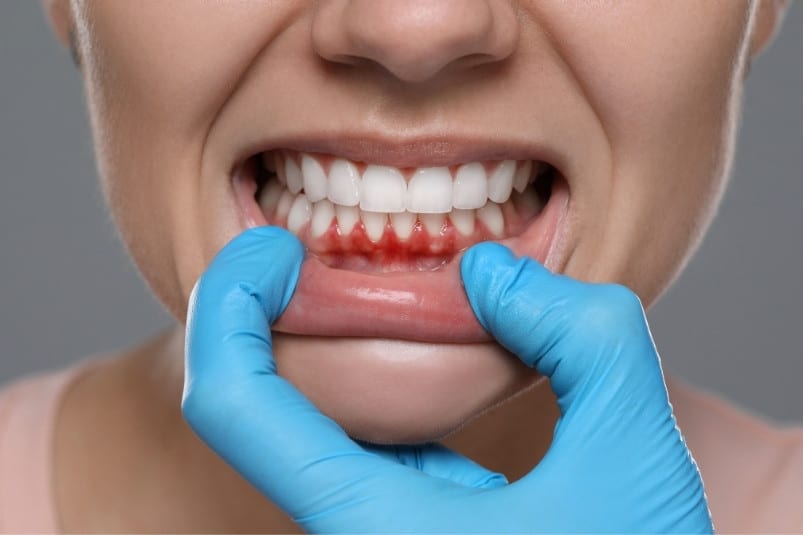
Understanding the Basics of Gum Health
Gum health begins with understanding the unique structure and function of your gums. The gums, or gingiva, form a protective barrier around teeth and underlying bone. This tissue is rich in blood vessels and connective fibers, making it highly sensitive to both bacterial invasion and inflammation. According to a 2022 study in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology, individuals with consistent gum maintenance routines experienced up to a 60% reduction in early signs of periodontal disease.
When exploring gum health, it is important to recognize common warning signs such as redness, swelling, bleeding during brushing, and persistent bad breath. These indicators, often subtle at first, can escalate if ignored. While plaque accumulation is the primary culprit, lifestyle factors like diet, stress, and sleep quality also significantly influence gum integrity.
The scientific community increasingly emphasizes the role of the oral microbiome in gum health. A balanced microbial environment supports immune responses and tissue repair. Conversely, disruptions often triggered by high sugar intake, smoking, or inadequate cleaning can lead to gingivitis and more advanced periodontal issues. Interestingly, research from the American Academy of Periodontology highlights that even small daily interventions can shift the microbial balance in favor of healthier gums, suggesting that maintenance is achievable for almost everyone.
Daily Practices to Strengthen Gum Health
Daily routines are critical for maintaining gum health, as even the most advanced dental treatments cannot fully compensate for inconsistent care. Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush helps remove plaque without damaging delicate gum tissue. The technique is equally important: gentle, circular motions along the gumline prevent trauma while ensuring thorough cleaning.
Flossing complements brushing by reaching areas where bristles cannot. Studies show that consistent flossing can reduce gingival inflammation by up to 40% over six months. For those seeking alternatives, interdental brushes or water flossers are also effective in maintaining gum integrity.
Hydration plays an often-overlooked role. Saliva acts as a natural cleanser, neutralizing acids and reducing bacterial load. Adequate water intake ensures sufficient saliva production, directly benefiting gum tissue. Additionally, limiting foods high in refined sugars and acids protects the gum surface from chronic irritation and microbial imbalance.
Beyond mechanical and dietary strategies, lifestyle habits like stress management, quality sleep, and avoiding tobacco products significantly impact gum health. Cortisol, the stress hormone, has been linked to reduced immune function in oral tissues, which can exacerbate inflammation. Meanwhile, regular physical activity supports systemic circulation, indirectly nourishing gum tissues and aiding their regenerative capacity.
The Role of Nutrition in Gum Health
Gum health is intimately connected with the nutrients we consume. Vitamins and minerals are not just optional; they provide the building blocks for tissue repair and immune function. For example, Vitamin C is crucial for collagen synthesis, directly supporting the structural integrity of the gums. Deficiency in this vitamin has been linked to increased gum bleeding and slower healing. Similarly, Vitamin D plays a role in moderating inflammation, while calcium and phosphorus strengthen the underlying jawbone that supports gum tissue.
| Nutrient | Impact on Gum Health | Sources |
| Vitamin C | Collagen synthesis, reduces bleeding | Citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries |
| Vitamin D | Anti-inflammatory, immune support | Sunlight, fortified dairy, fatty fish |
| Calcium | Bone strength, gum attachment | Milk, yogurt, leafy greens |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Anti-inflammatory, tissue repair | Salmon, walnuts, flaxseed |
Research shows that a diet rich in antioxidants, including polyphenols from green tea and berries, can modulate the oral microbiome, favoring bacteria that support gum health. While supplements can help, obtaining nutrients from whole foods is consistently more effective for long-term tissue resilience.
How Oral Hygiene Tools Influence Gum Health
Maintaining gum health is not only about what you do but also the tools you use. The right toothbrush, toothpaste, and flossing instruments can make a measurable difference. A soft-bristled brush reduces the risk of gum recession compared to hard bristles. Electric toothbrushes, particularly oscillating-rotating models, have been shown in multiple clinical trials to remove more plaque with less effort than manual brushing.
Toothpaste selection also matters. Formulations containing fluoride help prevent cavities that indirectly affect gum tissue, while agents like stannous fluoride or triclosan can reduce gingival inflammation. Interdental brushes and water flossers reach areas that regular floss may miss, particularly around tightly spaced teeth or dental restorations.
Interestingly, studies from the International Journal of Dental Hygiene suggest that alternating between different flossing tools can reduce microbial accumulation more effectively than using a single method, hinting at the importance of varied mechanical strategies in preserving gum health.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Gum Health
Gum health is influenced by more than just diet and brushing. Lifestyle choices, including sleep patterns, physical activity, and stress management, significantly impact oral tissues. Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can suppress the immune system and increase inflammation in gum tissues. Meanwhile, sleep deprivation has been linked to higher levels of inflammatory markers in the mouth, contributing to gingivitis and slower healing.
Tobacco use is another major factor. Nicotine constricts blood vessels, reducing nutrient flow to the gums, while smoke alters the oral microbiome in ways that favor harmful bacteria. Even moderate alcohol consumption can exacerbate gum inflammation through dehydration and chemical irritation.
Regular physical activity, conversely, supports circulation, ensuring that gums receive sufficient oxygen and nutrients. Researchers suggest that people who exercise regularly show lower rates of periodontal disease, possibly due to both improved blood flow and reduced systemic inflammation.
The Science Behind Gum Disease Prevention
Preventing gum disease is central to maintaining gum health. Plaque and tartar accumulation triggers gingivitis, which can progress to periodontitis if untreated. Modern research emphasizes that early intervention is key; inflammation is reversible in its initial stages, but prolonged bacterial invasion can lead to irreversible tissue and bone loss.
Advanced imaging techniques, such as 3D periodontal scans, allow clinicians to detect subtle changes in gum attachment levels before visible symptoms occur. Biomarkers in saliva, including inflammatory proteins and bacterial DNA, are also being explored as predictive tools for gum disease progression. These scientific insights highlight that proactive care not just reactive treatment is the most effective way to sustain gum health.
The Connection Between Systemic Health and Gum Health
Maintaining gum health is not an isolated goal; it intersects with overall systemic wellness. Studies have shown correlations between periodontal disease and conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and even cognitive decline. Chronic oral inflammation can trigger systemic inflammatory responses, potentially affecting blood vessels and metabolic processes.
For instance, patients with poorly maintained gums often exhibit higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, a marker for systemic inflammation. Conversely, interventions that improve gum health including professional cleaning and consistent home care can lower these markers, suggesting a feedback loop between oral and general health. This connection underscores why gum maintenance should be considered an integral part of holistic wellness strategies.
Behavioral Tips to Support Long-Term Gum Health
Beyond diet, hygiene, and lifestyle, certain behavioral patterns can reinforce gum health. These include:
- Routine dental visits – Professional assessments help detect early gum changes.
- Mindful brushing and flossing – Focused attention ensures thorough plaque removal.
- Hydration and saliva management – Chewing sugar-free gum stimulates saliva, which naturally protects gums.
- Oral habit tracking – Apps or journals can reinforce consistent care habits.
Behavioral reinforcement is supported by behavioral science: creating small, repeatable actions leads to sustainable improvements. Even minor adjustments, such as changing toothbrush heads every three months or rinsing after meals, cumulatively enhance gum resilience.
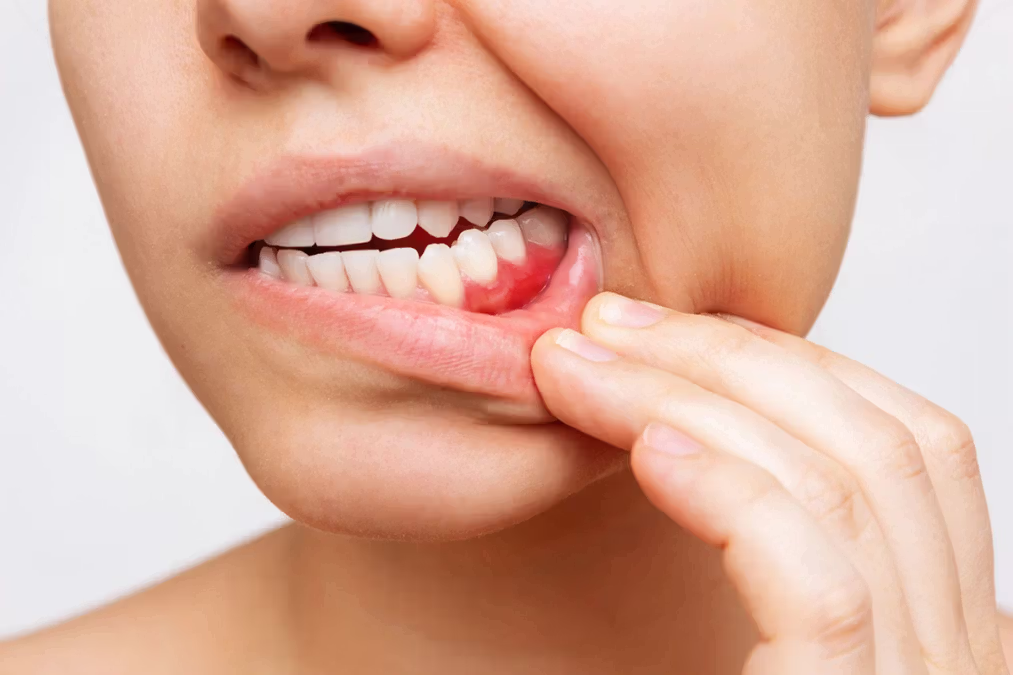
Innovations in Gum Health Monitoring
Maintaining gum health has entered a new era with technological innovations. Modern dental care increasingly relies on smart devices and digital tracking systems that monitor plaque buildup, gum inflammation, and brushing efficiency. For example, AI-powered toothbrushes can detect areas missed during brushing and adjust vibration intensity to optimize cleaning. Similarly, mobile apps now allow patients to log oral care routines, track bleeding episodes, and even upload photos for professional review.
Salivary diagnostics is another emerging tool. Researchers are developing portable saliva tests that detect inflammatory markers and bacterial profiles, offering early warning signs for gingivitis or periodontitis. These innovations make it possible to approach gum health with precision, potentially reducing the reliance on reactive treatments and supporting long-term oral wellness.
Exploring Natural Remedies and Alternative Approaches
Interest in natural approaches to support gum health has grown in recent years. Plant-based extracts such as green tea polyphenols, aloe vera, and licorice root have shown anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties in controlled studies. For instance, rinsing with green tea extract has been linked to a reduction in plaque accumulation and gum redness.
While these remedies are promising, scientific consensus emphasizes that they are supplementary rather than replacements for conventional oral care. However, incorporating them into a daily regimen can enhance gum resilience and overall microbial balance. Integrating herbal rinses, oil pulling, or natural anti-inflammatory supplements offers a holistic approach for individuals seeking complementary strategies for gum health.
The Future of Gum Health Research
The field of gum health is rapidly evolving, with research increasingly focusing on the oral microbiome, genetic predispositions, and systemic connections. Current studies are exploring how personalized oral care, guided by microbiome profiles, can optimize outcomes for gum integrity. For example, individuals with a higher prevalence of Porphyromonas gingivalis a bacterium strongly associated with periodontitis may benefit from targeted antimicrobial strategies.
Additionally, regenerative therapies, including stem cell applications and bioengineered gingival tissue, hold promise for reversing advanced gum damage. Although still experimental, these innovations could redefine the possibilities of gum restoration and maintenance, making gum health a dynamic and evolving field of scientific inquiry.
Common Myths About Gum Health
Despite growing awareness, misconceptions about gum health persist. One common myth is that bleeding gums are normal when brushing. In reality, bleeding often indicates inflammation and early gum disease. Another misconception is that gum care is only necessary for adults; children and adolescents also require proactive gum maintenance to establish lifelong oral health habits.
Misunderstandings around natural remedies, such as assuming herbal products alone can replace brushing or flossing, can also jeopardize gum integrity. Addressing these myths with evidence-based insights empowers individuals to make informed choices and reinforces the importance of comprehensive strategies for gum health.
A Comprehensive Approach to Gum Health
Maintaining gum health is a multifaceted endeavor that combines scientific insight, daily practices, nutrition, lifestyle, and innovative technologies. From understanding the biological foundation of gum tissue to exploring advanced diagnostic tools, each aspect contributes to long-term resilience and function.
By integrating proper oral hygiene techniques, nutrient-rich diets, behavioral reinforcement, and emerging scientific innovations, individuals can support their gums in a sustainable and evidence-informed way. The interplay between oral and systemic health underscores the significance of gum maintenance, highlighting that attention to this often-overlooked area can have far-reaching benefits.
Ultimately, gum health is not a one-time goal but a lifelong commitment one that benefits not only the mouth but overall well-being. As research advances, new strategies and tools will continue to enhance our understanding, empowering individuals to take proactive steps and maintain resilient, vibrant gums for years to come.

 Dijital Performans Ajansı.
Dijital Performans Ajansı.