When discussing dental procedures, one question that often arises is how many teeth can be extracted simultaneously. Tooth extraction is one of the most common dental surgeries worldwide, ranging from single tooth removal to complex cases involving multiple teeth. Understanding the factors that determine how many teeth can be safely removed at once is essential for patients and practitioners alike.
Extraction decisions are influenced by oral health, patient age, bone density, and the presence of infection or decay. While modern dentistry allows for multiple teeth to be removed during a single session, each situation requires careful assessment. The balance between efficiency, comfort, and safety is key to planning a multi-tooth extraction.
What Will You Read?
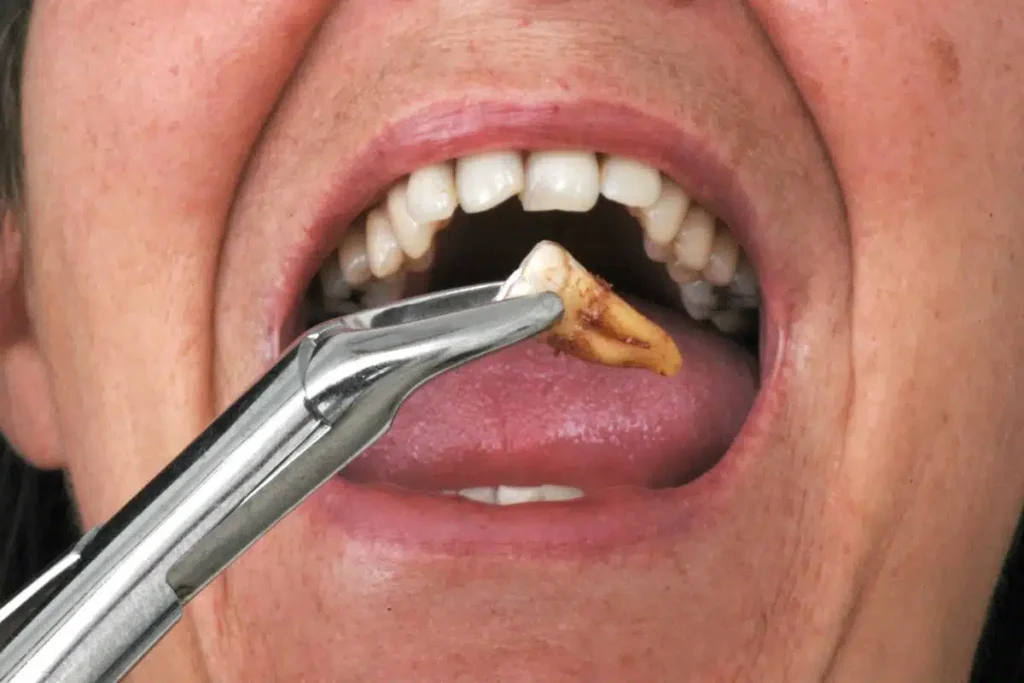
Factors Affecting Multi-Teeth Extraction
Several clinical and physiological factors dictate how many teeth can be removed in one procedure. Dentists must evaluate these before making a decision.
One major factor is the overall health of the patient. Conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular issues, or immune system weaknesses can limit the number of teeth extracted simultaneously. Another consideration is bone density and jaw structure. Dense or brittle bone can make multiple teeth extractions more challenging and riskier. Additionally, the position of the teeth, especially impacted or molars, affects how many can be safely removed in a single session.
Research published in the Journal of Oral Surgery indicates that adults with strong bone support may tolerate the removal of up to four or five teeth at once without significant complications. However, clinical judgment is always essential.
Types of Teeth Commonly Extracted Together
Not all teeth are equally likely to be removed in multi-tooth procedures. Certain categories are more predictable for simultaneous extraction.
- Wisdom teeth: Often extracted in groups due to impaction and alignment issues.
- Decayed molars: Large cavities or periodontal disease affecting adjacent molars can necessitate simultaneous removal.
- Orthodontic extractions: Sometimes multiple teeth are removed to facilitate braces or other orthodontic corrections.
This approach reduces repeated surgical sessions, minimizing discomfort and streamlining the healing process. However, dentists must evaluate potential risks such as swelling, bleeding, and jaw strain.
The Role of Sedation in Multi-Teeth Extraction
Removing several teeth at once can be stressful and painful without proper anesthesia. Sedation dentistry plays a critical role in multi-tooth procedures.
Options range from local anesthesia for small-scale extractions to intravenous sedation for more extensive work. Sedation ensures patient comfort, reduces anxiety, and allows the dentist to work efficiently. Studies in the International Journal of Dental Research show that patients undergoing multiple teeth extractions under sedation report significantly less post-operative discomfort and faster recovery times.
Recovery Considerations After Multi-Teeth Extraction
Recovery after removing multiple teeth is different from a single extraction. The body needs more time to heal, and post-operative care becomes crucial.
Patients may experience swelling, mild bleeding, and discomfort, especially when multiple teeth are extracted from both sides of the jaw. Nutrition also plays a key role; soft foods rich in protein and vitamins help tissue repair. According to a 2022 study in Oral Health and Preventive Dentistry, patients who followed structured recovery protocols had faster healing and fewer complications.
Additionally, oral hygiene must be maintained carefully. Gentle rinsing with saline or an antiseptic solution prevents infection. Dentists usually recommend avoiding vigorous brushing near extraction sites for at least a week to ensure proper clot formation and minimize dry socket risk.
Maximum Number of Teeth Extracted in a Session
How many teeth can safely be extracted at once depends on clinical judgment and patient tolerance. While some individuals may undergo removal of a single tooth, others can have several removed simultaneously.
In extreme cases, a full-mouth extraction may be performed, typically involving 28 to 32 teeth. This is more common in patients with advanced dental disease or preparing for complete dentures. However, the majority of multi-teeth extractions involve two to six teeth, balancing patient safety and surgical efficiency.
| Number of Teeth | Typical Scenario | Notes |
| 1-2 | Minor decay or infection | Quick recovery, low risk |
| 3-6 | Periodontal disease, orthodontics | May require sedation |
| 7+ | Extensive decay or impacted molars | High complexity, often under IV sedation |
| Full-mouth (28-32) | Severe dental disease | Requires full pre-op assessment and post-op care |
Risks of Multiple Teeth Extraction
While multi-teeth extraction can be efficient, it comes with potential risks. Understanding them helps patients make informed decisions.
Common issues include prolonged bleeding, swelling, and infection. The risk of dry socket increases when multiple teeth are removed, especially in the lower jaw. Nerve injury is also a consideration, particularly near wisdom teeth or molars. Research in Clinical Oral Investigations suggests that experienced oral surgeons minimize these risks through careful planning, imaging, and patient monitoring.
Some patients may experience jaw fatigue or discomfort due to prolonged opening during surgery. Dividing the procedure into multiple sessions is sometimes recommended if the patient’s tolerance is limited.
Long-Term Effects of Multi-Teeth Extraction
The long-term outcomes of removing multiple teeth depend on oral hygiene, follow-up care, and replacement strategies. Missing teeth can affect chewing efficiency, jaw alignment, and overall oral health if not managed properly.
Dental prosthetics such as bridges, partial dentures, or implants often follow multi-teeth extractions to restore function and aesthetics. Studies in Journal of Prosthodontics indicate that timely replacement reduces bone resorption and maintains facial structure. Additionally, maintaining strong oral hygiene and regular check-ups ensures the remaining teeth stay healthy and minimizes the risk of further extractions.
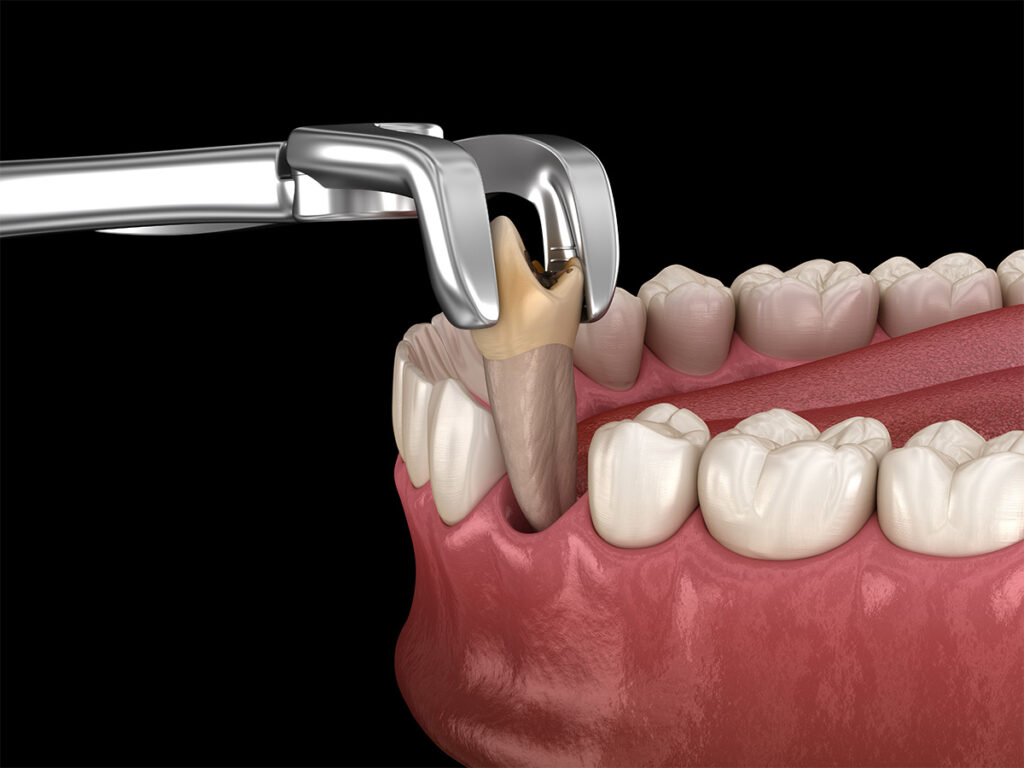
Alternatives to Multiple Teeth Extraction
Before committing to removing several teeth, dentists may explore alternative treatments. Preserving natural teeth is generally preferred when feasible.
Root canal therapy, periodontal treatment, or orthodontic adjustments can sometimes prevent the need for multiple teeth extractions. Additionally, minimally invasive procedures such as partial extraction or staged extraction sessions allow the patient to retain more natural teeth while managing dental disease. Evidence from International Endodontic Journal shows that strategic interventions often reduce the need for full multi-teeth extraction while still addressing infection or structural issues.
Planning and Consultation for Multi-Teeth Extraction
Careful planning is essential for any multi-teeth extraction procedure. Patients should consult with an experienced oral surgeon to discuss options, risks, and recovery expectations.
A thorough examination, including dental imaging and health assessment, helps determine the safest approach. Dentists consider factors such as age, systemic health, and the condition of surrounding teeth. By developing a personalized treatment plan, patients can undergo the procedure with minimal risk, optimized comfort, and better long-term outcomes.
Multi-teeth extraction is a complex but common dental procedure. The number of teeth removed simultaneously depends on patient health, dental condition, and surgical expertise. While removing multiple teeth can streamline treatment and reduce repeated appointments, careful planning, anesthesia, and post-operative care are essential to ensure successful outcomes.
By understanding factors such as recovery, risks, and alternatives, patients and dentists can make informed decisions. Whether it’s two adjacent molars or a full-mouth extraction, modern dentistry provides safe, effective, and tailored solutions for every scenario. Teeth removal, when performed thoughtfully, can lead to improved oral health, restored function, and long-lasting comfort.

 Dijital Performans Ajansı.
Dijital Performans Ajansı.