If you’ve ever come across the term Tetracycline Teeth, you might have wondered why certain teeth exhibit discoloration or unusual banding. Tetracycline Teeth is a phenomenon that occurs when the antibiotic tetracycline interacts with developing teeth, often leading to permanent staining. Understanding this condition requires delving into dental development, antibiotic mechanisms, and the historical use of tetracyclines in medicine.
What Will You Read?
What Causes Tetracycline Teeth?
The primary factor behind Tetracycline Teeth is the ingestion of tetracycline-class antibiotics during the formative years of teeth development. Tetracycline has a high affinity for calcium ions, which are abundant in developing teeth. When tetracycline binds to calcium in dentin and enamel, it causes discoloration that is often irreversible.
Research indicates that the timing of exposure plays a critical role. For example, children under the age of eight are more susceptible because their permanent teeth are still forming. Prenatal exposure can also lead to staining in primary teeth. Interestingly, Tetracycline Teeth may not always be purely aesthetic; in some cases, structural changes in enamel and dentin can occur, subtly affecting tooth integrity.
How Do Tetracycline Teeth Appear?
Tetracycline Teeth are recognized by their distinct color variations, which can range from yellow to gray or brown. The staining can manifest as horizontal bands, uniform discoloration, or a combination of both. Severity often depends on dosage, duration of exposure, and individual biological responses.
Advanced dental imaging studies suggest that the discoloration is due to the formation of tetracycline-calcium complexes in enamel during tooth mineralization. While some stains are mild and barely noticeable, others can significantly affect self-esteem and social perception. The degree of staining can vary across teeth in the same individual, making Tetracycline Teeth a visually complex condition.
Historical Context of Tetracycline Use and Dental Impact
Tetracycline antibiotics became widely used in the 1950s and 1960s, both in adults and children, for bacterial infections. At that time, awareness of their effects on developing teeth was limited. Historical data show a significant incidence of Tetracycline Teeth in cohorts exposed during that era.
Subsequent research and regulatory guidelines have restricted tetracycline use in children under eight and during pregnancy, substantially reducing new cases. Yet, studies continue to analyze residual impacts in adults who were exposed as children. This historical perspective provides insight into the interplay between pharmaceutical practices and long-term dental outcomes.
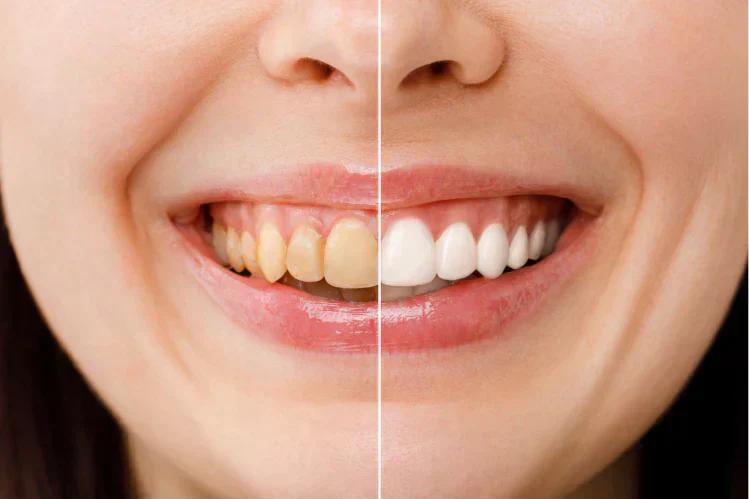

Diagnosis and Clinical Evaluation of Tetracycline Teeth
Dentists diagnose Tetracycline Teeth through visual examination, patient history, and in some cases, imaging techniques. A detailed medical history, particularly regarding antibiotic exposure during early childhood, is crucial for an accurate assessment.
Clinically, discoloration can be subtle or pronounced. Some studies recommend using spectrophotometric analysis to quantify staining levels, providing objective data that supports both diagnosis and treatment planning. Recognizing Tetracycline Teeth early helps dental professionals anticipate aesthetic concerns and discuss potential cosmetic interventions.
Management and Cosmetic Considerations
While the structural integrity of Tetracycline Teeth is usually unaffected, cosmetic concerns are common. Various management strategies exist, including:
- Professional whitening treatments, which may provide partial improvement
- Microabrasion techniques to reduce superficial discoloration
- Porcelain veneers or composite bonding for severe cases
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these interventions varies. Scientific literature emphasizes that early consultation with a dental professional is key to tailoring treatment to individual needs. In addition, some research explores experimental methods, such as laser-assisted bleaching, though long-term outcomes remain under study.
Psychological and Social Implications of Tetracycline Teeth
Beyond the aesthetic dimension, Tetracycline Teeth can influence psychological well-being. Research indicates that visible tooth discoloration may affect social interactions, self-confidence, and even professional opportunities. Studies suggest that individuals with noticeable dental staining often report heightened self-consciousness during adolescence.
Understanding the psychosocial dimension underscores why dental professionals consider both medical and cosmetic strategies. Addressing Tetracycline Teeth holistically requires integrating patient preferences, scientific evidence, and innovative techniques to enhance overall quality of life.
Prevention and Modern Guidelines
Today, prevention of Tetracycline Teeth relies primarily on judicious antibiotic prescribing. Regulatory bodies, including the American Dental Association and FDA, recommend avoiding tetracycline use in pregnant women and children under eight. Public health campaigns have also educated healthcare providers about long-term dental consequences.
Emerging research highlights the importance of monitoring alternative antibiotics and evaluating their effects on dental development. This proactive approach ensures minimal risk while preserving the efficacy of tetracyclines for bacterial infections in appropriate populations.
Tetracycline Teeth represents a unique intersection of pharmacology, dentistry, and developmental biology. While historically common, modern guidelines and awareness have significantly reduced new cases. The condition’s aesthetic impact, combined with its potential psychosocial effects, highlights the importance of comprehensive evaluation and individualized management strategies.
Through ongoing research and careful clinical observation, dental professionals continue to refine approaches to diagnosing and managing Tetracycline Teeth, ensuring both functional and aesthetic considerations are addressed. Whether for historical cases or contemporary prevention, understanding the science behind Tetracycline Teeth enriches our broader knowledge of dental development and antibiotic effects.

 Dijital Performans Ajansı.
Dijital Performans Ajansı.