Gum recession is a common dental concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth gradually wears away, exposing more of the tooth or its root. While it can be influenced by age, genetics, or oral hygiene habits, understanding what helps with gum recession is essential for anyone looking to maintain both oral health and a confident smile. Research and clinical observations suggest that there are multiple approaches ranging from lifestyle adjustments to professional care that can support gum integrity and reduce further recession.
What Will You Read?
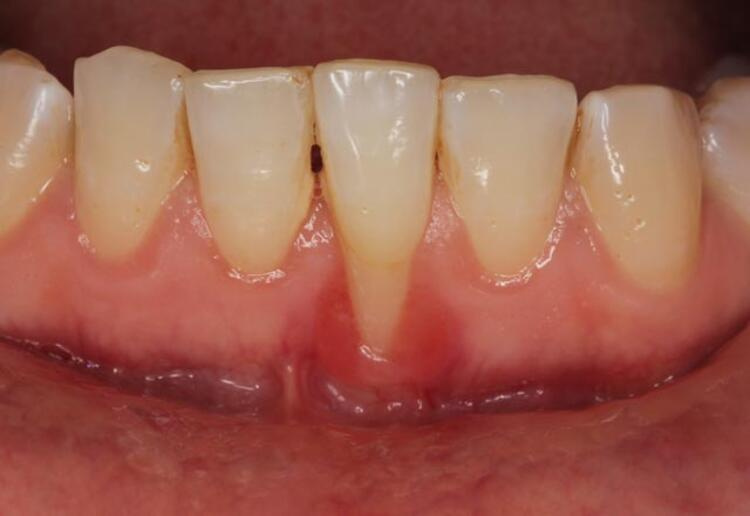
Understanding the Causes of Gum Recession
Gum recession is not just a cosmetic issue; it can indicate underlying dental problems. One of the main causes is aggressive tooth brushing. People often think harder brushing cleans better, but this can actually wear away delicate gum tissues over time. Other factors, such as periodontal disease, tobacco use, and genetic predisposition, also play a significant role. Interestingly, studies suggest that up to 30% of adults over 30 experience some level of gum recession, highlighting its prevalence.
Dental researchers have observed that teeth misalignment or bruxism (teeth grinding) can exacerbate gum wear. When the gums are exposed to chronic mechanical stress, the tissue may recede more rapidly. Understanding these triggers is critical because addressing the root cause can slow down or even prevent further gum recession. Beyond mechanical and genetic factors, systemic health issues like diabetes and hormonal changes in women can influence gum health, making it a multifactorial concern.
The Role of Oral Hygiene in Managing Gum Recession
When it comes to gum recession, daily oral care plays an essential role. Brushing twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and using gentle, circular motions can prevent unnecessary gum wear. Equally important is flossing, which removes plaque between teeth without injuring the gums. Studies consistently indicate that proper oral hygiene not only reduces the risk of gum disease but also slows the progression of existing gum recession.
Mouthwashes containing antibacterial agents may provide additional protection. They help reduce bacterial load in hard-to-reach areas, which can minimize inflammation and subsequent gum tissue loss. While toothpaste with fluoride is primarily aimed at preventing cavities, some formulations also contain ingredients that strengthen gum tissue. Maintaining a balanced oral care routine, therefore, is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to support gum health.
Professional Treatments for Gum Recession
Gum recession can reach a point where home care alone is insufficient, and professional intervention becomes essential. Dentists and periodontists offer a variety of treatments aimed at halting progression and, in some cases, restoring lost gum tissue. One widely recognized approach is scaling and root planing, a deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar buildup beneath the gumline. Research indicates that patients who undergo this procedure experience measurable reductions in gum inflammation, which indirectly slows gum recession.
For more advanced cases, surgical options such as gum grafts are considered. These procedures use tissue from the patient’s palate or donor tissue to cover exposed roots. Clinical studies suggest that grafting can improve not only aesthetics but also tooth sensitivity and long-term gum stability. Other innovative treatments include regenerative techniques that encourage the growth of new gum tissue using biologically active materials. While not all patients are candidates for surgery, these interventions provide evidence-based pathways to manage severe gum recession effectively.
Natural Approaches to Supporting Gum Health
Many individuals explore natural methods to complement professional care for gum recession. Nutrient-rich diets, rich in vitamin C, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, are shown to support gum tissue integrity. Vitamin C, in particular, is essential for collagen synthesis, a key protein in gum structure. Studies have demonstrated that patients with sufficient vitamin intake exhibit slower progression of gum recession and reduced gum inflammation.
Herbal remedies and oils are also commonly discussed in dental research. Aloe vera, green tea extracts, and oil pulling with coconut oil have been explored for their anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. While clinical evidence varies, anecdotal reports suggest they may help reduce plaque accumulation and soothe irritated gums. Additionally, staying hydrated and avoiding excessive sugar can indirectly protect gum health by minimizing the oral environment that fosters bacterial overgrowth, a significant contributor to gum recession.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Gum Recession
Lifestyle choices have a profound impact on the progression of gum recession. Smoking, for instance, is strongly correlated with both gum disease and tissue loss. Research indicates that nicotine restricts blood flow to the gums, impairing healing and making them more susceptible to recession. Similarly, chronic stress can influence gum health through hormonal changes that increase inflammation, potentially accelerating gum recession.
Sleep patterns, physical activity, and oral habits like teeth grinding (bruxism) also play a role. Patients with bruxism often experience faster gum tissue wear due to mechanical stress. Using night guards, managing stress through mindfulness techniques, and adopting regular exercise routines can all contribute to healthier gums. Even subtle habits, like avoiding overly acidic or abrasive foods, have been linked to slower rates of gum recession, highlighting that everyday choices can significantly influence long-term oral health outcomes.
Nutrition and Its Impact on Gum Recession
Gum recession can be influenced significantly by nutrition. Diets high in processed sugars and refined carbohydrates promote bacterial growth, which accelerates gum inflammation and tissue breakdown. Conversely, foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts can mitigate oxidative stress in gum tissues. Studies have shown that individuals consuming adequate levels of vitamin C, vitamin K, and calcium often have stronger, more resilient gums, reducing the likelihood of severe gum recession.
Probiotics are another emerging area of interest. Oral probiotics, containing beneficial bacterial strains, may help maintain microbial balance in the mouth. Early research suggests they can reduce plaque buildup and gingival inflammation, indirectly supporting gum tissue health. While probiotics are not a standalone solution, when combined with proper oral hygiene, they may contribute to slower progression of gum recession and overall periodontal health.
Technological Advances in Gum Recession Management
Modern dentistry offers innovative technologies for managing gum recession. Laser therapy, for example, is used to reduce bacterial load in periodontal pockets and stimulate tissue regeneration. Clinical trials indicate that patients receiving laser-assisted treatments often experience less post-procedural discomfort and faster recovery compared to traditional methods. Additionally, imaging technologies, including 3D scans and digital periodontography, allow dentists to precisely assess gum loss, enabling more targeted and effective interventions.
Regenerative biomaterials are also transforming treatment approaches. Biocompatible scaffolds and growth factor-enriched gels are used to encourage new tissue formation in areas affected by gum recession. While still developing, these technologies promise minimally invasive options for patients seeking both functional and aesthetic improvements. The integration of AI-based monitoring systems is another fascinating development, allowing continuous tracking of gum health through smart devices and predictive analytics.
Preventive Strategies for Long-Term Gum Health
Preventing gum recession is often more manageable than reversing it. Consistent oral hygiene practices including soft brushing, proper flossing techniques, and periodic professional cleanings form the foundation of prevention. Regular dental checkups allow early detection of gum changes, enabling interventions before significant tissue loss occurs. Studies consistently show that patients adhering to preventive strategies exhibit slower progression of gum recession over time.
Lifestyle adjustments further enhance prevention. Avoiding tobacco, moderating alcohol consumption, and managing systemic conditions like diabetes contribute to healthier gums. Stress reduction techniques, including yoga or mindfulness, can also decrease inflammation that might otherwise accelerate gum recession. Even simple modifications, such as using a soft toothbrush or switching to non-abrasive toothpaste, can make a measurable difference in maintaining gum tissue integrity over the long term.

The Link Between Oral Microbiome and Gum Recession
Emerging research highlights the critical role of the oral microbiome in gum recession. A balanced microbial environment supports gum tissue health, while dysbiosis an imbalance in oral bacteria can trigger inflammation and tissue degradation. Advanced sequencing studies have identified specific bacterial strains strongly associated with accelerated gum recession, suggesting potential for targeted microbial therapies in the future.
Maintaining a healthy oral microbiome involves both diet and hygiene. Fermented foods, reduced sugar intake, and careful plaque management are strategies shown to foster beneficial bacteria. Additionally, new mouth rinses and gels containing prebiotic compounds are being explored for their ability to support microbial balance, offering a novel dimension in the management of gum recession.
Long-Term Outlook and Research Insights
Understanding gum recession requires both clinical observation and longitudinal research. Evidence suggests that while some degree of gum recession may be inevitable with aging, proactive care can significantly slow its progression. Studies indicate that combining professional treatment, proper oral hygiene, and lifestyle interventions leads to better outcomes than any single approach alone.
Researchers continue to explore genetic predispositions, regenerative therapies, and microbiome-focused interventions. The integration of personalized dental care, predictive analytics, and minimally invasive procedures may soon redefine how gum recession is managed. Patients who remain informed and engaged in their oral health journey are most likely to experience sustained gum stability and overall dental well-being.
Navigating Gum Recession with Knowledge
Gum recession is a multifactorial condition influenced by genetics, oral habits, systemic health, and lifestyle choices. While it can present aesthetic and functional challenges, understanding what helps with gum recession empowers individuals to take a proactive role in their oral care. From nutritional strategies and lifestyle adjustments to advanced dental treatments and emerging technologies, a combination of approaches offers the best chance of preserving gum tissue and oral health over time.
By staying informed and prioritizing consistent care, individuals can navigate gum recession not as an inevitable decline, but as a manageable aspect of lifelong oral wellness. Scientific insights, when combined with daily habits and professional guidance, transform how gum recession is perceived from a problem to a challenge that can be strategically addressed.

 Dijital Performans Ajansı.
Dijital Performans Ajansı.